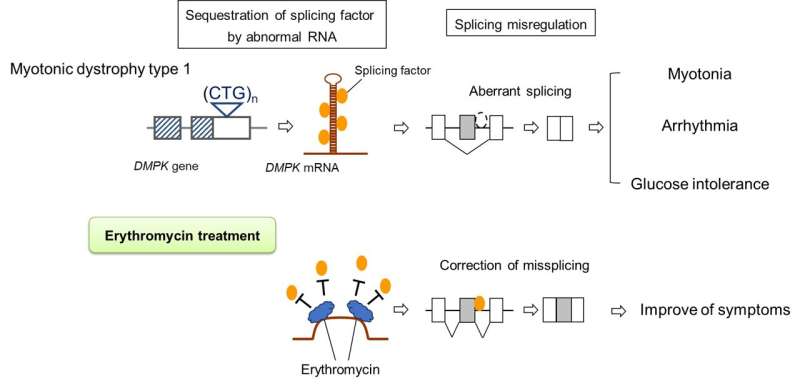
Myotonic dystrophy kind 1 (DM1) is a genetic illness characterised by progressive muscular weak spot. There’s presently no remedy regardless of many latest efforts. However now researchers from Japan might have discovered a treatment.
In a examine revealed in eClinicalMedicine, researchers from Osaka College have reported an revolutionary method to establish a potential new remedy for DM1, which has simply handed section 2 scientific testing with flying colours.
DM1 is the most typical type of muscular dystrophy. It’s brought on by a genetic mutation that impacts a vital course of often known as different splicing, which is vital for appropriately assembling proteins everywhere in the physique. On this manner, DM1-causing mutations have an effect on many various bodily methods, resulting in a variety of signs which can be troublesome to deal with.
To establish potential therapies for DM1, the analysis workforce used drug repositioning screening, a way by which medication which can be already used for a particular objective are examined for his or her results on different ailments. They discovered that erythromycin—which you’ll already be aware of, given its widespread use as an antibiotic—could also be efficient in DM1 due to its potential for bettering splicing abnormalities.
“After our profitable preclinical trials in DM1 cell and mouse fashions, we had excessive hopes for erythromycin,” says Masayuki Nakamori, lead writer of the examine. “As the subsequent step in getting this drug to the clinic, we performed a trial on 30 individuals with DM1 to check the remedy’s security and tolerability, with a secondary goal of investigating its efficacy.”
The researchers gave 6 of the 30 sufferers a placebo, whereas 12 obtained a low dose (500 mg) and 12 obtained a excessive dose (800 mg) of erythromycin for twenty-four weeks. As a result of these long-term doses are already used for different ailments, the researchers hoped that the protection knowledge can be constructive—and thankfully, they had been proper.
“We had been additionally very all in favour of testing the efficacy of erythromycin in sufferers with DM1,” explains Masayuki Nakamori. “To do that, we primarily checked out markers of aberrant splicing immediately in sufferers’ muscle biopsies.”
Though this efficacy testing revealed few vital outcomes, the analysis workforce famous that a number of sufferers who obtained erythromycin confirmed main enhancements in splicing markers, suggesting that some sufferers reply higher than others. Additional evaluation additionally revealed that some splicing markers had been considerably improved at one dose of erythromycin however not the opposite, indicating that dosage could also be vital.
Regardless of the small pattern dimension, the researchers are very optimistic. Erythromycin continues to be a promising therapeutic possibility, and subsequent section 2b and three trials must be carried out as quickly as possible to see whether or not this extensively used antibiotic can efficiently deal with DM1, or no less than a subset of sufferers.
Extra data:
Masayuki Nakamori et al, Erythromycin for myotonic dystrophy kind 1: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, section 2 trial, eClinicalMedicine (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.102390
Osaka College
Quotation:
Off-label use of a typical antibiotic to deal with muscular dystrophy (2023, December 27)
retrieved 27 December 2023
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.







