Though main open-angle glaucoma (POAG) is the main explanation for blindness in individuals over the age of 55, there stays no remedy for the illness and its organic mechanisms usually are not effectively understood. Elevated intraocular strain (IOP) is a significant threat issue for the illness, however many sufferers with glaucoma have regular eye strain and nonetheless lose imaginative and prescient.
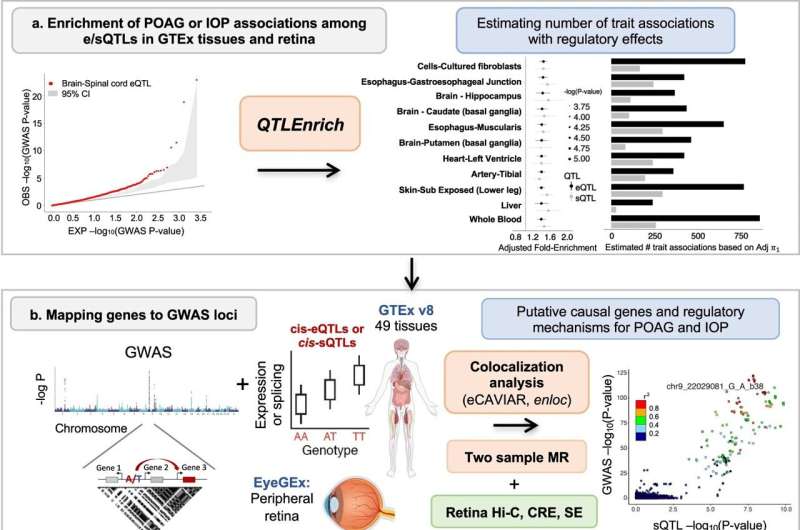
In a brand new examine printed this previous month in Nature Communications, researchers from Mass Eye and Ear, led by Ayellet Segrè, Ph.D., performed a complete examine that mixed genetic discoveries from a big cross-ancestry genome-wide affiliation examine meta-analysis of POAG, led by Janey Wiggs, MD, Ph.D., and a big meta-analysis of IOP with genetic regulation research and single cell expression measurements in glaucoma-relevant eye tissues.
In doing so, they uncovered key genes, organic processes, and cell varieties that will have an effect on the pathogenesis of POAG in IOP-dependent and impartial manners.
Utilizing integrative analyses, they recognized a whole bunch of genes and regulatory results underlying over 100 loci related to POAG and/or IOP that will contribute to glaucoma threat by means of altered gene expression ranges. These genes are enriched in organic pathways implicated in illness mechanisms, together with elastic fiber formation and extracellular matrix group, vascular improvement, and neuronal-related processes.
Moreover, by using single-nucleus gene expression information from the aqueous humor outflow pathways, retina, and the optic nerve head and surrounding posterior tissues, as a part of a cell atlas of the entire eye led by Josh Sanes, Ph.D. from the Division of Molecular and Mobile Biology at Harvard College, the researchers recognized identified and fewer well-established cell varieties by which gene dysregulation might have an effect on optic nerve degeneration.
This included fibroblasts within the typical and unconventional outflow pathways, astrocytes within the retina and optic nerve head, oligodendrocytes and vascular cells within the optic nerve head, and fibroblasts within the surrounding area of the optic nerve head.
Pathways recognized of their evaluation can impression varied constructions within the eye, pointing to quite a few potential mechanisms that may work together with completely different genes and cell varieties that will contribute to POAG. These findings present new insights concerning gene expression and post-transcriptional gene regulation that would enhance drug design for glaucoma.
“Our work has generated new insights into POAG mechanisms, which may inform the event of novel therapies concentrating on IOP discount and neuroprotection,” stated Segrè.
“For instance, this analysis means that concentrating on neuronal assist cells, along with retinal ganglion cells, could also be essential to contemplate within the design of recent drug and cell therapies. Via our ongoing work geared toward detecting genetic regulation of gene expression in glaucoma-relevant eye tissues, we hope sooner or later, to offer a extra full understanding of POAG threat and IOP variation.”
Extra info:
Andrew R. Hamel et al, Integrating genetic regulation and single-cell expression with GWAS prioritizes causal genes and cell varieties for glaucoma, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-44380-y
Mass Basic Brigham
Quotation:
Researchers determine genes and cell varieties that will have causal function in main open-angle glaucoma formation (2024, February 16)
retrieved 16 February 2024
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.







