Of the greater than 3,000 extramural K99 awards granted between 2008 and 2021, none had been to an investigator at a Traditionally Black Faculty or College (HBCU), primarily based on a brand new evaluation revealed in eLife.
“I feel that information level speaks volumes, particularly when you think about that 11 HBCUs have R2-status—signifying excessive analysis exercise—and a number of other could receive R1-status, signifying very excessive analysis, exercise within the subsequent yr or two. The inequities are staggering, however sadly not shocking,” mentioned Nicole Woitowich, Ph.D., Medical Social Sciences and govt director on the Northwestern College Scientific and Translational Sciences (NUCATS) Institute.
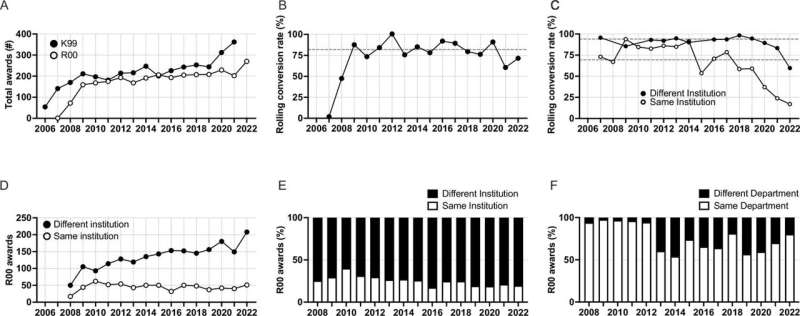
Reviewing Nationwide Institutes of Well being (NIH) K99/R00 awards and the profession development of awardees, investigators additionally discovered that researchers with larger mobility, males and people employed at well-funded establishments expertise larger subsequent funding success.
Investigators used information from the NIH Grants Administration Database to disclose the inequalities that form college funding alternatives and profession pathways. Inequalities had been discovered to disproportionately have an effect on ladies and school working at specific establishments, together with HBCUs.
“Our hope is that policymakers and directors at funding establishments take discover and attempt to assist those that are systemically deprived. We all know that most individuals usually are not shocked by our findings however by getting the exhausting information on the market, we hope that tangible modifications will be made,” mentioned lead writer Daniel Tyrrell, Ph.D., assistant professor of Molecular and Mobile Pathology on the College of Alabama at Birmingham.
“One perspective for college directors could possibly be that they need to rent extra cell males to extend probabilities of future funding. An alternate technique is to raised assist these with much less mobility and girls. This may be executed by way of coverage round pay fairness, depart, childcare, understanding mobility limitations and extra.”
The analysis workforce included Sarah Hengel, Ph.D., Tufts College; Christopher Solis, Ph.D., MBA, Florida State College; Tauras Vilgalys, Ph.D., College of Chicago; and Joel Babdor, Ph.D., College of Pennsylvania. Their collaboration and subsequent publication arose after a Tweet posted by Tyrrell, who shared a preprint of his preliminary findings.
“After I noticed his preprint, I used to be instantly taken with analyzing the info by gender,” Woitowich mentioned. “I despatched him a message, as did my co-authors, expressing curiosity on this work. We got here collectively, every brining a special analytical lens to this dataset. It is a prime instance of how social media can foster collaboration and community constructing in science.”
The NIH Pathway to Independence program is designed to supply as much as 5 years of assist by way of two phases of funding. The preliminary, or mentored part (K99) gives one to 2 years of mentored assist to promising postdoctoral analysis scientists. The K99 part is adopted by as much as three years of impartial assist (R00) contingent on the scientist securing an impartial analysis place.
Evaluation confirmed that the cumulative benefit of K99/R00 funding is stark.
Males who moved to a brand new establishment with massive NIH funding portfolios throughout the R00 part had the shortest median time to receiving a subsequent main NIH award (4.6 years) and had a larger total probability of ever receiving a serious award (84.6%).
Every cumulative drawback elevated the median time to obtain a serious NIH award by about six months and decreased the general probability to obtain subsequent main NIH award by 5% to six%.
The median time to obtain subsequent main NIH awards for K99/R00 awardees that had been ladies that stayed at an R00 establishment with smaller NIH funding portfolios was 7.4 years with only a 60% probability to obtain a serious NIH award.
“These information spotlight how vital early-career assist is for biomedical scientists and communicate extra broadly to the disparities that persist,” Woitowich mentioned. “I feel it is vital that we seize and consider this information so we are able to no less than have a benchmark for progress.”
This size of time is essential for tenure-track college who usually have between six and 7 years to earn tenure, which regularly hinges on receipt of a serious analysis grant for research-intensive college. These cumulative disadvantages could contribute to decrease chance of receiving promotion and tenure and should contribute to the gender disparities in college ranks and in management positions.
“There are systemic issues that should be executed to assist course appropriate, however there are additionally small issues that may change, too,” Tyrrell mentioned “We are likely to name the minority of highly-NIH-funded establishments ‘prestigious’ however this apply propagates the destructive perception that the remaining establishments usually are not prestigious. It is a incorrect mind-set. We, as lecturers and people could make aware choices to attempt to change this attitude and doubtlessly influence this apply.”
Extra info:
Nicole C Woitowich et al, Evaluation of NIH K99/R00 awards and the profession development of awardees, eLife (2024). DOI: 10.7554/eLife.88984.4
Northwestern College
Quotation:
Evaluation of analysis grants pipeline illustrates systematic disadvantages (2024, February 21)
retrieved 21 February 2024
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.







