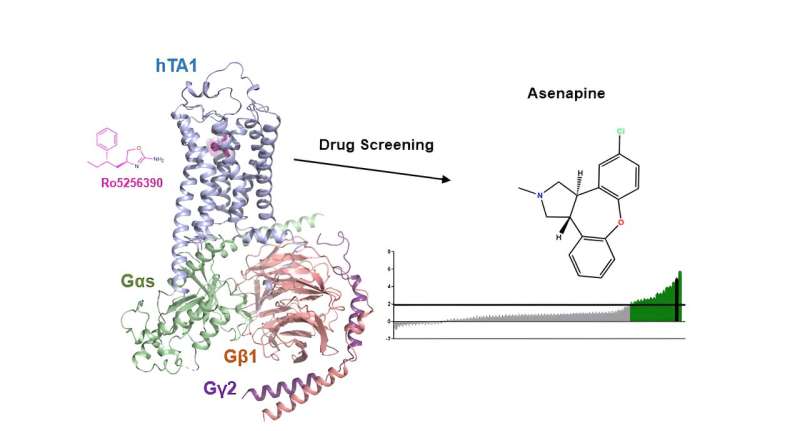
Researchers on the Icahn College of Drugs at Mount Sinai have uncovered insights into the potential mechanism of motion of the antipsychotic remedy asenapine, a doable therapeutic goal for substance use and neuropsychiatric issues. This discovery could pave the best way for the event of improved drugs focusing on the identical pathway.
Their findings, revealed in Nature Communications, present {that a} mind protein often called the TAAR1 receptor, a drug goal identified to control dopamine signaling in key reward pathways within the mind, differs considerably in people in comparison with the preclinical rodent fashions on which medicine are sometimes examined.
The examine suggests contemplating species-specific variations in drug-receptor interactions and additional investigation into methods asenapine impacts the physique as steps towards potential therapeutic enhancements.
“In investigating the purposeful and structural properties of TAAR1, our examine aimed to shed extra gentle on its mechanisms and pharmacology,” says examine first creator Gregory Zilberg, a Ph.D. candidate at Icahn Mount Sinai. “Our findings could information the event of novel TAAR1 medicine and immediate extra exploration of medicines just like asenapine.”
Utilizing superior strategies to research TAAR1’s construction and performance, the researchers recognized three essential components. First, there are variations between rodent and human TAAR1 that seemingly have an effect on how preclinical mannequin research could be translated to people. Second, TAAR1 is far more carefully associated to serotonin and dopamine receptors than beforehand assumed. This means that a number of serotonin-targeting drugs may need unknown therapeutic efficacy or uncomfortable side effects which might be, the truth is, because of their actions at TAAR1.
Lastly, the investigators spotlight that the clinically used antipsychotic asenapine unexpectedly reveals sturdy activation of TAAR1, suggesting, the truth is, that this serotonin- and dopamine-targeting antipsychotic may derive a few of its therapeutic results from TAAR1 activation.
If confirmed in additional research, this might open up new potentialities for its potential in different TAAR1-related therapeutic purposes, similar to its use in substance use issues, in addition to the event of recent asenapine-based medicine.
The researchers famous the absence of details about variations in how TAAR1 works in rodents and people and emphasised that a few of these variations may account for why preclinical knowledge on TAAR1 has not but been efficiently translated into efficient therapies in people. Subsequent, the researchers plan to review the place TAAR1 is positioned inside cells and what its exact position is in influencing serotonin and dopamine signaling.
“This examine offers a major leap in understanding TAAR1, providing potential avenues for drug growth and inspiring additional analysis into its therapeutic purposes,” says senior creator Daniel Wacker, Ph.D., Assistant Professor of Pharmacological Sciences, and Neuroscience, at Icahn Mount Sinai.
“As our work advances, we anticipate it might play an important position in shaping the event of recent medicine focusing on TAAR1 and providing priceless insights into how medicine just like asenapine may work.”
Extra data:
Gregory Zilberg et al, Molecular foundation of human hint amine-associated receptor 1 activation, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-44601-4
The Mount Sinai Hospital
Quotation:
Demystifying a key receptor in substance use and neuropsychiatric issues (2024, January 2)
retrieved 2 January 2024
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.







